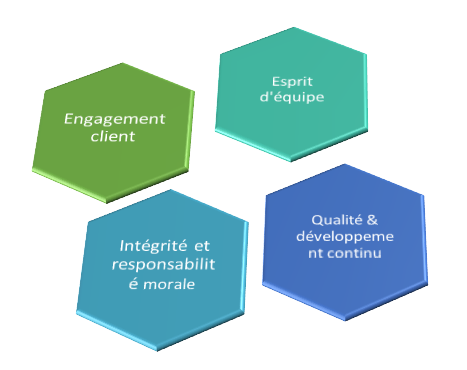
Nos valeurs
Qualité & développement continu
Nous fournissons d'excellents produits en plus d'un service distingué
Engagement client
Nous développons des relations positives avec nos clients
Intégrité et responsabilité morale
Nous adhérons aux normes d'intégrité les plus élevées dans toutes nos activités. Nous nous considérons moralement et responsables du respect de nos obligations
Esprit d'équipe
Nous travaillons ensemble, au-delà des frontières, pour répondre aux besoins de nos clients et aider l'entreprise à s'améliorer